Design and Development of Visually Guided Autonomous Quadrotors: application in surveillance and disaster management
PI: Professor Laxmidhar Behera, Department of Electrical Engineering
Co-PI: Professor Sumana Gupta, Department of Electrical Engineering
Professor K.S. Venkatesh, Department of Electrical Engineering
Professor Nishchal Vema, Department of Electrical Engineering
 The need for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with greater maneuverability and hovering ability for various military and civilian applications has led to the current rise in quadrotor research. A quadrotor, also called a quadrotor helicopter or quadcopter, is a multi-copter that is lifted and propelled by four rotors. The four-rotor design allows quadrotors to be relatively simple in design yet highly reliable, agile and maneuverable.
The need for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with greater maneuverability and hovering ability for various military and civilian applications has led to the current rise in quadrotor research. A quadrotor, also called a quadrotor helicopter or quadcopter, is a multi-copter that is lifted and propelled by four rotors. The four-rotor design allows quadrotors to be relatively simple in design yet highly reliable, agile and maneuverable.
 Development of a Visually Guided Quadrotor The concept of Localization is used for maintaining the quadrotor at a particular point in 3Dspace. In Figure 1, we demonstrate visual control of a quadrotor (Pelican from AscTec) for hovering at a specific altitude where the current position is obtained by looking at a predefined
Development of a Visually Guided Quadrotor The concept of Localization is used for maintaining the quadrotor at a particular point in 3Dspace. In Figure 1, we demonstrate visual control of a quadrotor (Pelican from AscTec) for hovering at a specific altitude where the current position is obtained by looking at a predefined
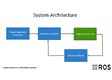
pattern present on the ground. The control architecture is shown in Figure 2.
 A very real life application of this experiment lies in rescue operations during the event of an environmental disaster. A quadrotor can enter a damaged building and move to places which would otherwise be difficult to access by rescue teams.
A very real life application of this experiment lies in rescue operations during the event of an environmental disaster. A quadrotor can enter a damaged building and move to places which would otherwise be difficult to access by rescue teams.
Visual Navigation of a Quadrotor
Single camera is used to reduce the payload and increase the endurance of the system. The two frames, displaced in time, are taken to simulate the stereo vision for
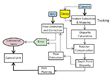
computing the depth of the target/scene. To calculate the correspondence between two frames, feature points detected from the images are matched. We can calculate the disparity between matched points caused by UAV movement by taking the difference between the two coordinate positions in the scenes. Since the UAV can also undergo rotation, we compensate for disparity caused by rotation. The scheme is provided in Figure 3
 Stabilization of Multi-UAV systems and Formation Control Formation of quadrotors has great applications in precision agriculture, disaster management and crowd control. We consider an n-agent system where the agents move on a plane. Each agent communicates with its neighbours. The communication topology is fixed and is represented by a completely connected graph G. The objective of this work is to develop a control law to achieve a desired formation. The control law comprises of two parts: Improve collision
Stabilization of Multi-UAV systems and Formation Control Formation of quadrotors has great applications in precision agriculture, disaster management and crowd control. We consider an n-agent system where the agents move on a plane. Each agent communicates with its neighbours. The communication topology is fixed and is represented by a completely connected graph G. The objective of this work is to develop a control law to achieve a desired formation. The control law comprises of two parts: Improve collision
 avoidance scheme (ICAS) and consensus term. The ICAS has been designed to avoid collision between agents, and the consensus term helps in achieving the desired formation.
avoidance scheme (ICAS) and consensus term. The ICAS has been designed to avoid collision between agents, and the consensus term helps in achieving the desired formation.
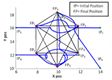
We consider a 6-agent systemto generate the collision free desired hexagon formation. Figure-4 is presented the trajectories of the six agents and from figure 5 it is observed that no agents collide with each other as the minimum inter agent distances never goes less than the safety distance rin=0.5
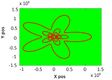 Static and Dynamic Boundary Estimation and Tracking: We consider 2n-agent system where the agents move on a plane. Each ith agent can communicate with its two neighbouring agents (Backward and Forward agents). The communication topology is fixed and is represented by a connected graph G. Each ith actual agent is associated with (i+1)th virtual agent (odd index is for actual agents and even index is for the corresponding virtual agent). The objective of this work is to develop a boundary tracking and estimation algorithm
Static and Dynamic Boundary Estimation and Tracking: We consider 2n-agent system where the agents move on a plane. Each ith agent can communicate with its two neighbouring agents (Backward and Forward agents). The communication topology is fixed and is represented by a connected graph G. Each ith actual agent is associated with (i+1)th virtual agent (odd index is for actual agents and even index is for the corresponding virtual agent). The objective of this work is to develop a boundary tracking and estimation algorithm
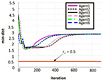
 to track the static and dynamic boundary. In this work we are assuming that velocity of the dynamic boundary is less than the agent's velocity. We consider 24-agent system, where 12 are actual agents and 12-are virtual agents. Figure 6 presents the evolution of the dynamic boundary.
to track the static and dynamic boundary. In this work we are assuming that velocity of the dynamic boundary is less than the agent's velocity. We consider 24-agent system, where 12 are actual agents and 12-are virtual agents. Figure 6 presents the evolution of the dynamic boundary.
From figure 7, it is observed that the agents are converging to the boundary.