Abhinav Prakash, Krishanu Biswas and Somnath Bhowmick
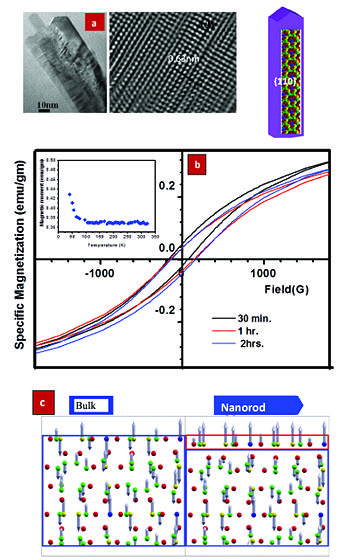
In the periodic table, Mn is located just before the ferromagnetic family of metals, namely, iron, cobalt and nickel. However, it's allotrope at room temperature (a-Mn) is known to be paramagnetic. Thus, at room temperature, Mn cannot achieve the magnetic strength of its fellow ferromagnetic metals. Magnetism in ferromagnetic metals can be described in terms of direct exchange interaction, where the coupling strength depends on the ratio (l) of the inter-atomic distance to the radius of d-shell of an atom in a material. In case of Mn, lvalue is just below 1.5, which is slightly less than that for its ferromagnetic neighbors. This implies that, increasing the separation between Mn atoms will favorably alter the ratio and leading to ferromagnetism. This is normally achieved either by alloying Mn with a non-magnetic element or by growing epitaxial layer of Mn on Fe or Co or Ni. The ferromagnetic ternary alloys containing Mn, known as Heusler alloys (such as Cu2MnAl) are typical examples of the first type. The other way of imparting ferromagnetism in Mn is by a technique in which an epitaxial layer of Mn grown on Fe (100) exhibits a net magnetic moment.
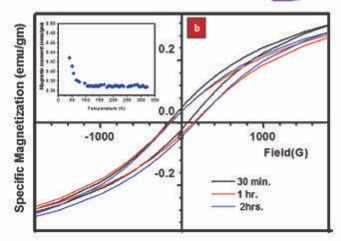
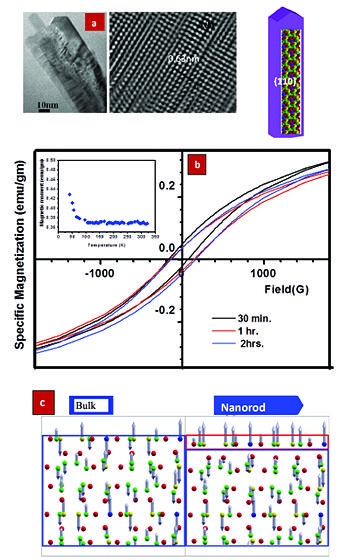
However, it may be possible to induce ferromagnetism in pure metallic a-Mn by altering the morphology of the Mn crystallites, i.e. preparing 1D nanostructure. We report the ferromagnetic order in pure and freestanding a-Mn nanorods prepared by ball milling at low temperature (152K). The bulk a-Mn is known to be a complicated system with Mn having a tendency towards anti-ferromagnetic order. It is worthwhile to note thatSchull and Wilkinson 16 have demonstrated earlier that Mn can undergo transition from paramagnetic to anti-ferromagnetic state below its Neel temperature of 100K. However, there is no report in the literature on ferromagnetic behaviour of either bulk or nano-structured a-Mn. We observe for the first time that, indeed, ferromagnetic order can be induced in the nanorods, which can be explained by considering surface magnetism. The DFT calculations indicates that the origin of such ferromagnetism is due to surface atoms that are less coordinated, giving rise to ferromagnetic surface with antiferromagnetic core.
Reference:
J. App. Physics, 121, 2017, 084304